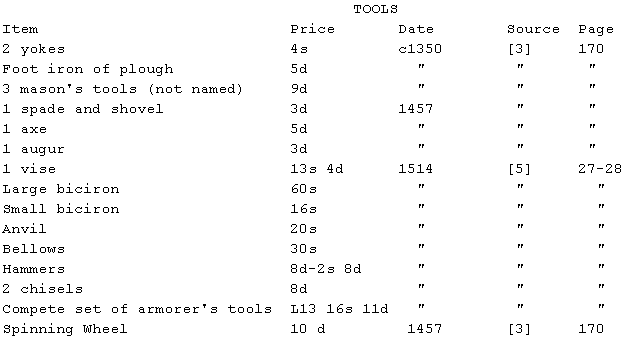
List of prices of medieval items
Courtesy of Kenneth Hodges (hodges@jif.berkeley.edu)
The list of medieval prices which follows is by no means complete or
thoroughly researched; I merely extracted references from some of the
books I have, and I thought others might like to inspect it. The sources
I used are listed at the end. If an item is listed several times, it is
because I had several references I wished to record.
Money goes as follows:
1 pound (L) = 20 shillings (s)
1 crown = 5 shillings
1 shilling = 12 pence (d)
1 penny = 4 farthings
1 mark = 13s 4d
The French Livre, sou, and denier are equivalent to the pound, shilling
and penny (Latin liber, solidus, and denarius, I believe, which is where
the weird English abbreviations come from).
For ease, I've divided this list into the following sections: tools,
horses, food and livestock, books and education, buildings, cloth and
clothing, armor, weapons, marriage, funerals, travel, miscellaneous
goods, and wages.
Of course, a price list is a misleading guide to a feudal economy,
because so many goods were either produced within a household, or
supplied by a lord. Retainers could get money, but they would also get
food, lodging, weapons (sometimes), and cloth. Knights Templar were
provided with clothes, horses, and armor.
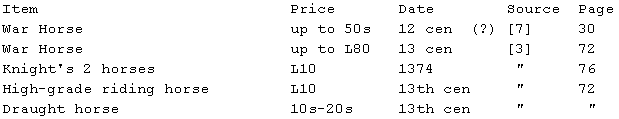 Note: Horse prices varied dramatically; for instance, they doubled
between 1210 and 1310. ([3], p. 37).
Note: Horse prices varied dramatically; for instance, they doubled
between 1210 and 1310. ([3], p. 37).
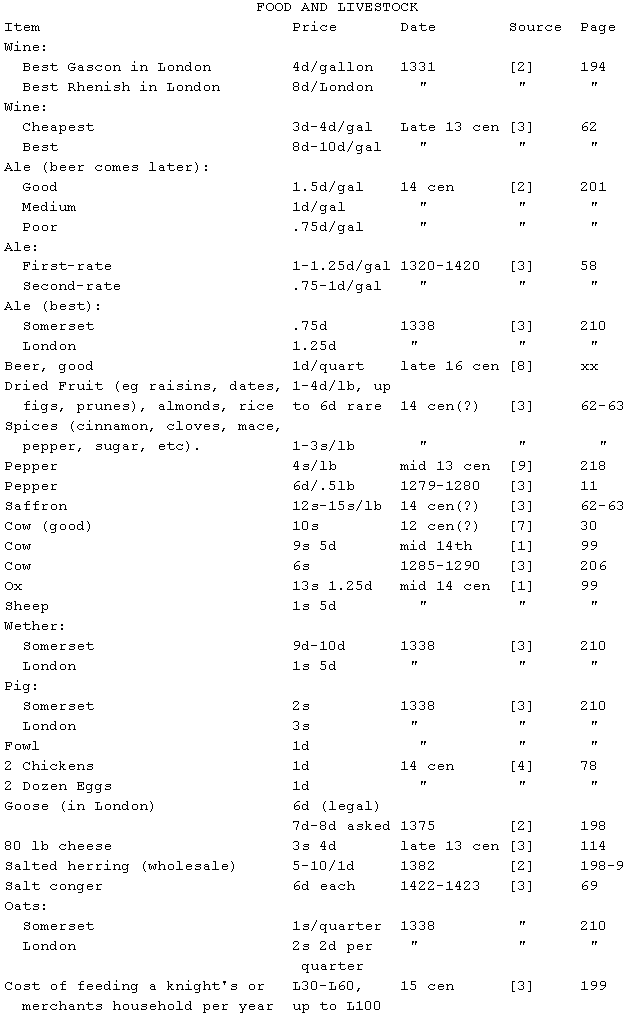 Related note: around 1380, these are the average costs per day of feeding
people on an estate ([3], p. 65): lord, 7d; esquire, 4d; yeoman, 3d; and
groom, 1d.
Related note: around 1380, these are the average costs per day of feeding
people on an estate ([3], p. 65): lord, 7d; esquire, 4d; yeoman, 3d; and
groom, 1d.
 * Source says 2s/day. This is not only insanely high, but the text also
claims that the board was the same as at Oxford--i.e., 2s/week or
104s/year.
** A pecia is 16 columns of 62 lines of 32 letters, i.e., 31 744 letters,
or about 7 500 - 8 000 words. Rental period is not specified, but I
would guess a year; books were rented to be copied, and copying the Bible
took 15 months. See [9], p. 172.
* Source says 2s/day. This is not only insanely high, but the text also
claims that the board was the same as at Oxford--i.e., 2s/week or
104s/year.
** A pecia is 16 columns of 62 lines of 32 letters, i.e., 31 744 letters,
or about 7 500 - 8 000 words. Rental period is not specified, but I
would guess a year; books were rented to be copied, and copying the Bible
took 15 months. See [9], p. 172.
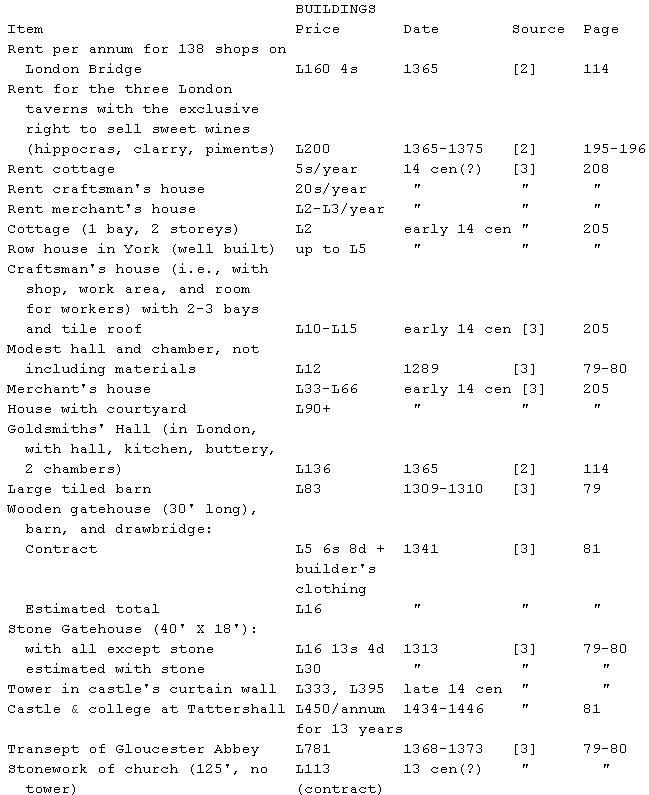 note: tithes were often calculated at 1d a week for every 20s of annual
rent paid (4, p. 208).
The following are the estimates of raw materials and labor that went into
the tower of Langeais, a rectangular, tapering stone tower built in 992-
994. The source is [6], pp. 47ff. The dimensions at the base were 17.5
meters by 10 meters; the height was 16m (3 floors); the walls were 1.5m
thick, made of two shells filled with loose rock.
note: tithes were often calculated at 1d a week for every 20s of annual
rent paid (4, p. 208).
The following are the estimates of raw materials and labor that went into
the tower of Langeais, a rectangular, tapering stone tower built in 992-
994. The source is [6], pp. 47ff. The dimensions at the base were 17.5
meters by 10 meters; the height was 16m (3 floors); the walls were 1.5m
thick, made of two shells filled with loose rock.

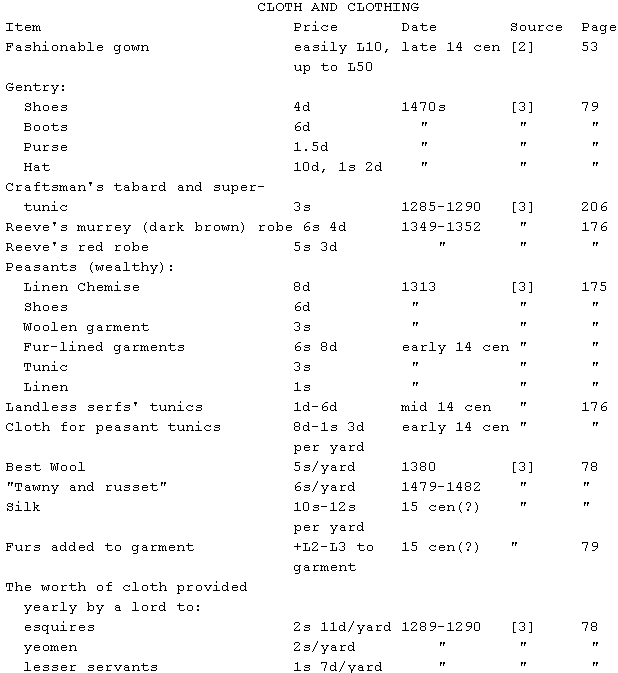 Note: loose tunics take 2.25-2.5 yards. In the late 14th century,
shorter doubled (lined) tunics, known as doublets, became fashionable,
requiring 4 yards ([3], pp 175,176).
Note: loose tunics take 2.25-2.5 yards. In the late 14th century,
shorter doubled (lined) tunics, known as doublets, became fashionable,
requiring 4 yards ([3], pp 175,176).
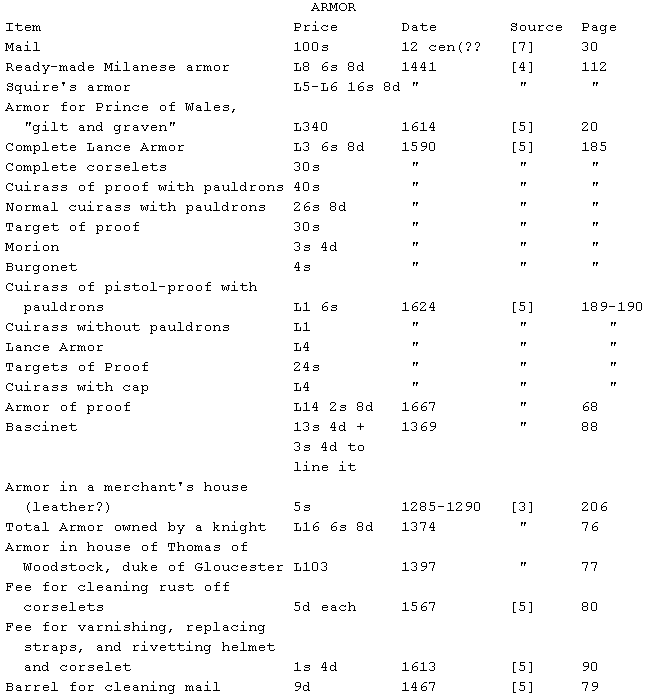
Note: mail is chainmail; almost all the rest is plate-armor. The armor
of the knight in 1374 was probably mail with some plates; same for
Gloucester's. Mail was extremely susceptible to rust, and was cleaned by
rolling it in sand and vinegar in a barrel. Pauldrons are shoulder
plates; morions are open helms, burgonets and bascinets closed helms; and
a target refers to any of a number different kind of shields. Armor of
proof is tested during the making with blows or shots from the strongest
weapons of the time; if a weapon is listed, the armor does not claim to
be proof against everything, only that it is proof up to that weapon's
strength (eg pistol proof is not musket proof, but may be sword proof).
All plate armor was lined with cloth, to pad the wearer, quiet the armor,
and reduce wear between the pieces. This, along with the necessary
straps, was a significant amount of the expense. An armorer asking for
money to set up shop in 1624 estimated production costs and profit for a
number of different types of armor: I give two examples below ([5], pp.
189-190).


Note: Sorry, folks, that's all I found. It was mandatory in England for
all freemen to own certain types of weapons and armor. (In 1181 every
freeman having goods worth 10 marks (1 mark = 13s 4d) had to have a mail
shirt, a helmet, and a spear. All other freemen should have helmet,
spear, and gambeson (quilted armor) [4], p. 39.) Later, the government
stored arms and armour in churches for use; in the 13th century anyone
with an income of L2-L5 (wealthy peasants) had to have bows; archery
practice became compulsory on Sundays and holidays. You may know that
the extreme range of the longbow was 400 yards, but did you know that a
statute of Henry VIII no one over 24 could practice at a range of less
than 220 yards? (See [4], p. 95 and elsewhere).
Note: for guessing prices, see the section on tools (an axe for 5d). An
armorer might make 24s a month; say a week to make a decent sword, and
you might get a price that way. See the section on books and education
for fencing instruction.
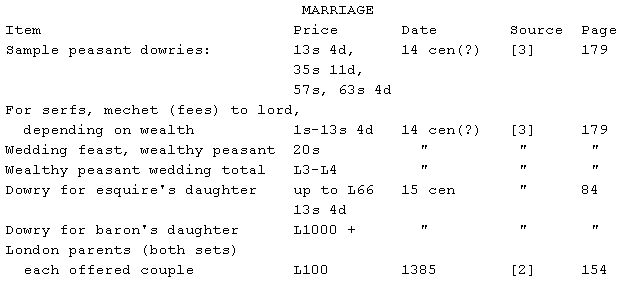 Note: these costs will be wildly varying depending on circumstance.
Note: these costs will be wildly varying depending on circumstance.
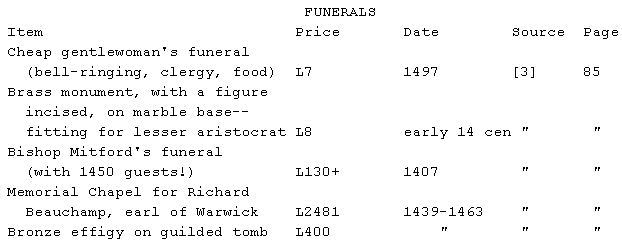 Note: Christopher Dyer gives as a rough rule of thumb 1 year's income for
a funeral ([3], p. 85)
Note: Christopher Dyer gives as a rough rule of thumb 1 year's income for
a funeral ([3], p. 85)
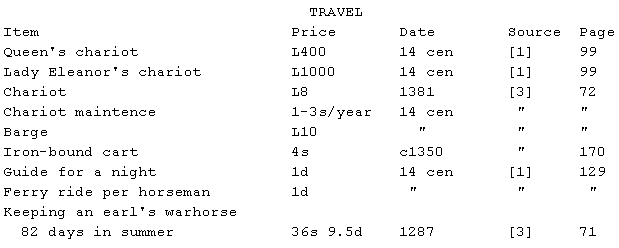 Note: [1], pp 126-129, gives the following prices at an inn in 1331. For
one day, 3 men with 4 servants spent: Bread, 4d; beer, 2d; wine 1.25d;
meat, 5.5d; potage, .25d; candles, .25d; fuel, 2d; beds, 2d; fodder for
horses, 10d. The four servants staying alone sleep 2 nights for 1d.
Generally, all 7 spend 2d a night on beds; in London, it is 1d per head.
Note: [1], pp 126-129, gives the following prices at an inn in 1331. For
one day, 3 men with 4 servants spent: Bread, 4d; beer, 2d; wine 1.25d;
meat, 5.5d; potage, .25d; candles, .25d; fuel, 2d; beds, 2d; fodder for
horses, 10d. The four servants staying alone sleep 2 nights for 1d.
Generally, all 7 spend 2d a night on beds; in London, it is 1d per head.
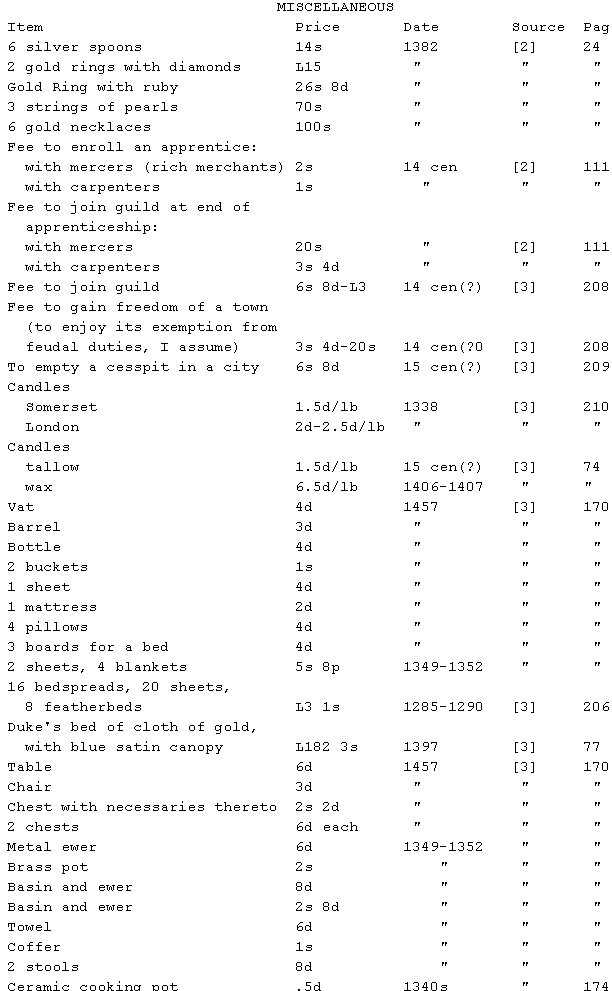 Note: most of these come from inventories of peasants' belongings. The
fine goods would be more expensive.
Note about lighting: great houses could use 100 lb of wax and tallow in a
single winter night ([3], p. 74). Others, not as rich, would go to sleep
earlier.
Note: most of these come from inventories of peasants' belongings. The
fine goods would be more expensive.
Note about lighting: great houses could use 100 lb of wax and tallow in a
single winter night ([3], p. 74). Others, not as rich, would go to sleep
earlier.
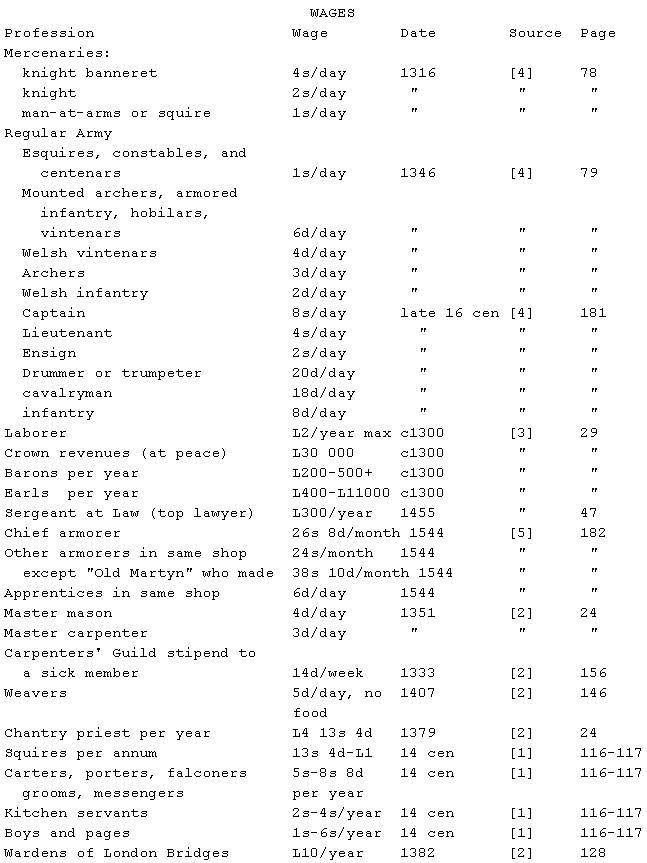 Note: sheriffs of London paid 300L per year, hoping to make a profit from
the fines they collected.
Note: 30 adult sheep could produce about 20s of wool per year in 1299
([3], p. 114).
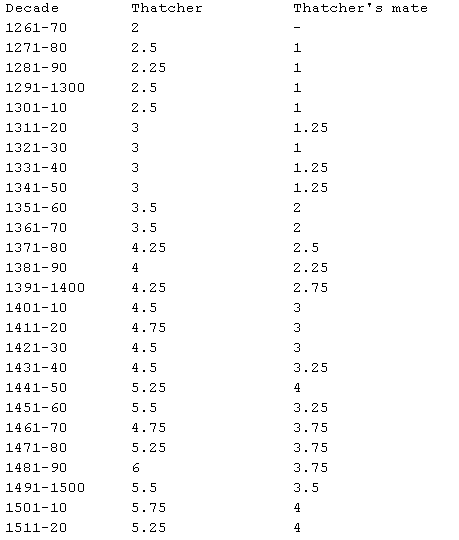
Note: To get a VERY ROUGH sense of money, I reproduce the following chart
from Dyer ([3], p. 206). These are averages of daily wages in pence.
Note: sheriffs of London paid 300L per year, hoping to make a profit from
the fines they collected.
Note: 30 adult sheep could produce about 20s of wool per year in 1299
([3], p. 114).
Note: To get a VERY ROUGH sense of money, I reproduce the following chart
from Dyer ([3], p. 206). These are averages of daily wages in pence.
[1] English Wayfaring Life in the XIVth Century, J. J. Jusserand, trans
Lucy Smith, Putnam's Sons, New York,1931 (Orig. 1889).
[2] London in the Age of Chaucer, A. R. Myers, University of Oklahoma
Press, Norman, 1972
[3] Standards of Living in the Later Middle Ages, Christopher Dyer,
Cambridge University Press, 1989
[4] English Weapons & Warfare, 449-1660, A. V. B. Norman and Don
Pottinger, Barnes & Noble, 1992 (orig. 1966)
[5] The Armourer and his Craft from the XIth to the XVIth Century,
Charles ffoulkes, Dover, 1988 (orig. 1912)
[6] "The Cost of Castle Building: The Case of the Tower at Langeais,"
Bernard Bachrach, in The Medieval Castle: Romance and Reality, ed.
Kathryn Reyerson and Faye Powe, Kendall/Hunt, Dubuque, Iowa, 1984
[7] The Knight in History, Frances Gies, Harper & Row, New York, 1984
[8] Methods and Practice of Elizabethan Swordplay, Craig Turner and
Tony Soper, Southern Illinois University Press, Carbondale, 1990
[9] Life in a Medieval City, Joseph and Frances Gies, Harper & Row,
New York, 1969
 | to Medieval Resources |
 | to Middle English Literature |
 | to Luminarium Encyclopedia |
 | to Luminarium Main |
Site copyright ©1996-2023 Anniina Jokinen. All Rights Reserved.
Copying of the site source code and/or content is expressly prohibited.
Links and printing for personal or classroom use are acceptable.
Last updated on February 24, 2023.